Hearts and Minds
Follow Your Heart, or Your Heart Follows?
Matlab Stata empirical study data analysis cardiac tracking sensor dataGoal
The body shows the emotions of people: when people are happy they smile, when they are sad they cry. According to James-Lange theory, this also works the other way around: the body shows an emotion and, because of this, the emotional state of the person is changed.
Emotions and heartbeat are related: when emotion changes the heartbeat changes as well. Combined with the James-Lange theory, if the heartbeat, or the perception of the heartbeat, is changed, this might also change the emotion state of people.
In this study, we aimed to find out whether the presence of haptic cardiac feedback (i.e., mimic the perception of one’s own heartbeat) influence the physiological state and psychological perception of different stimuli.
Research questions
- Can people’s exciting/stress level be influenced by haptic cardiac feedback?
Experiment
Participant
79 participants, 50 females and 29 males (26.1 years old ± SD = 9.3 years).
Design
- Between-subject design
- 2 conditions: no haptic cardiac feedback (control) and haptic cardiac feedback (feedback).
Materials
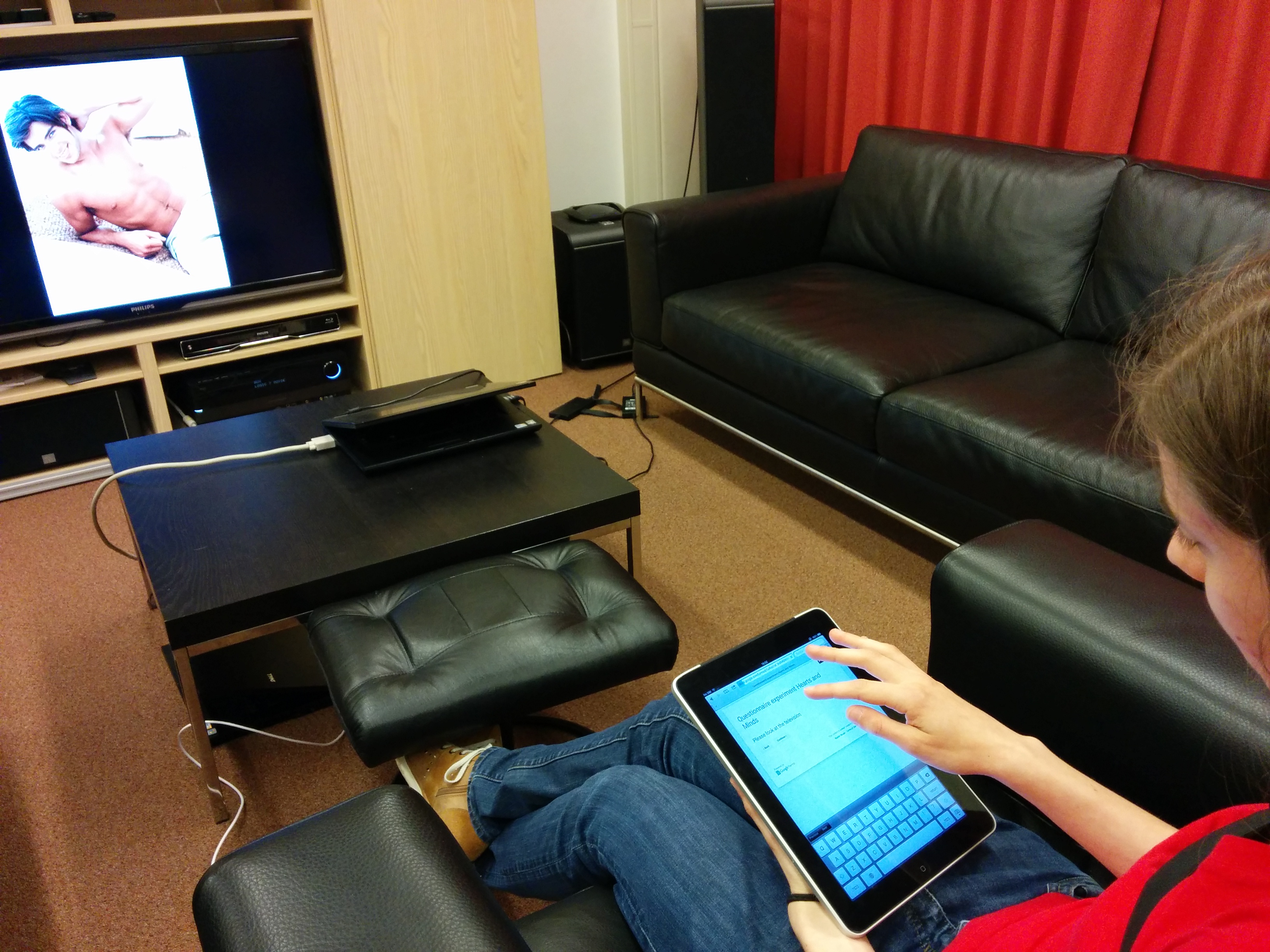
The experiment was conducted in an isolated room with speakers, a TV, and a tablet (to control TV), in order to mimic a typical living room.
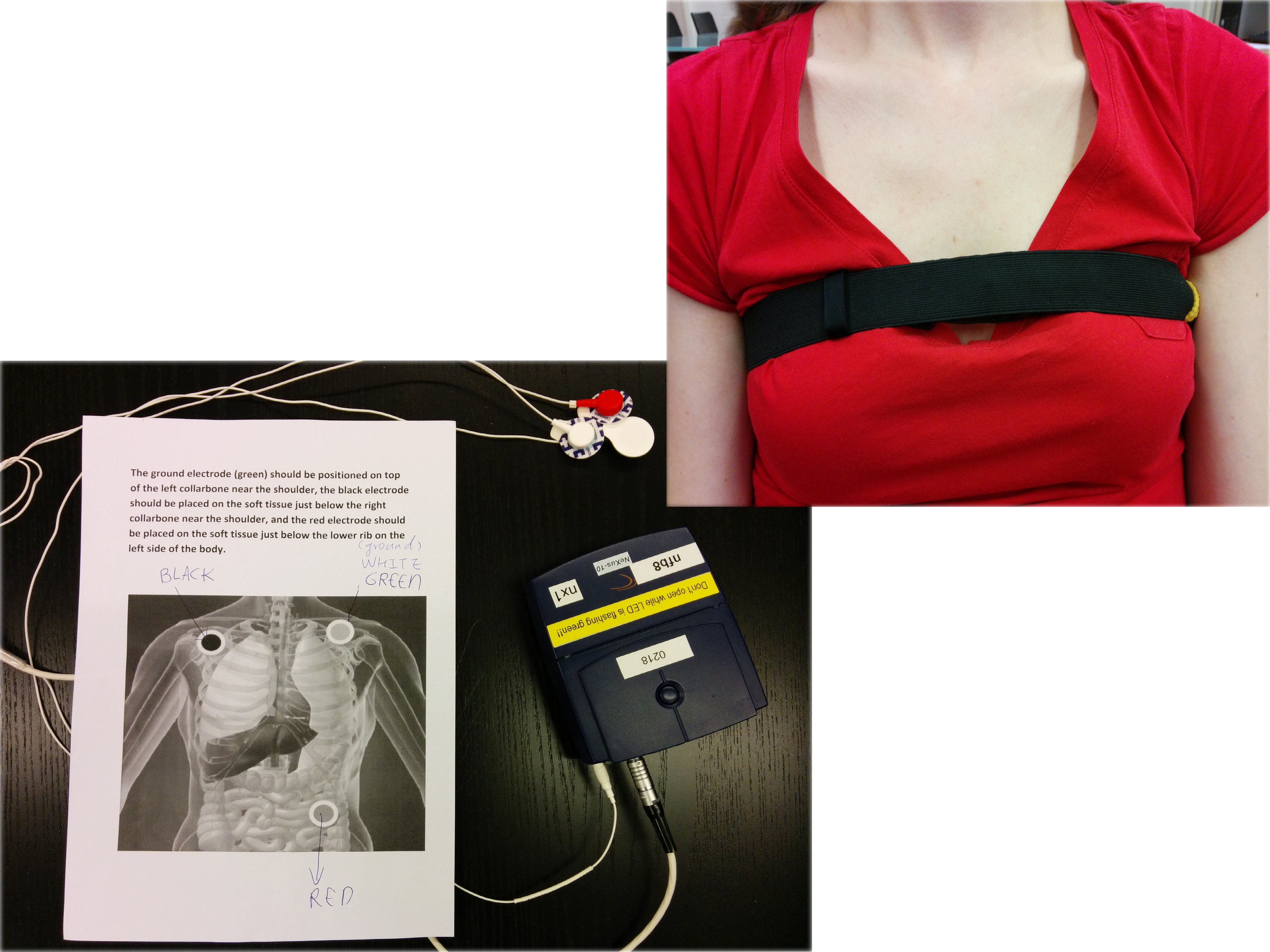
Participatns were asked to attach Mobi interface (heartbeat measurement device) and a Tactilizer. The Mobi interface was used for the collection of ECG data. The Tactilizer was incorporated in an elastic strap and contained four small motors that produce vibrations in synchrony with the heartbeat of the participants, thus simulating their own heartbeat through haptic feedback. The participants weared the strap just above the chest, with the four motors on the left upper part of the chest, on top of the location where the heart is.

Stimuli
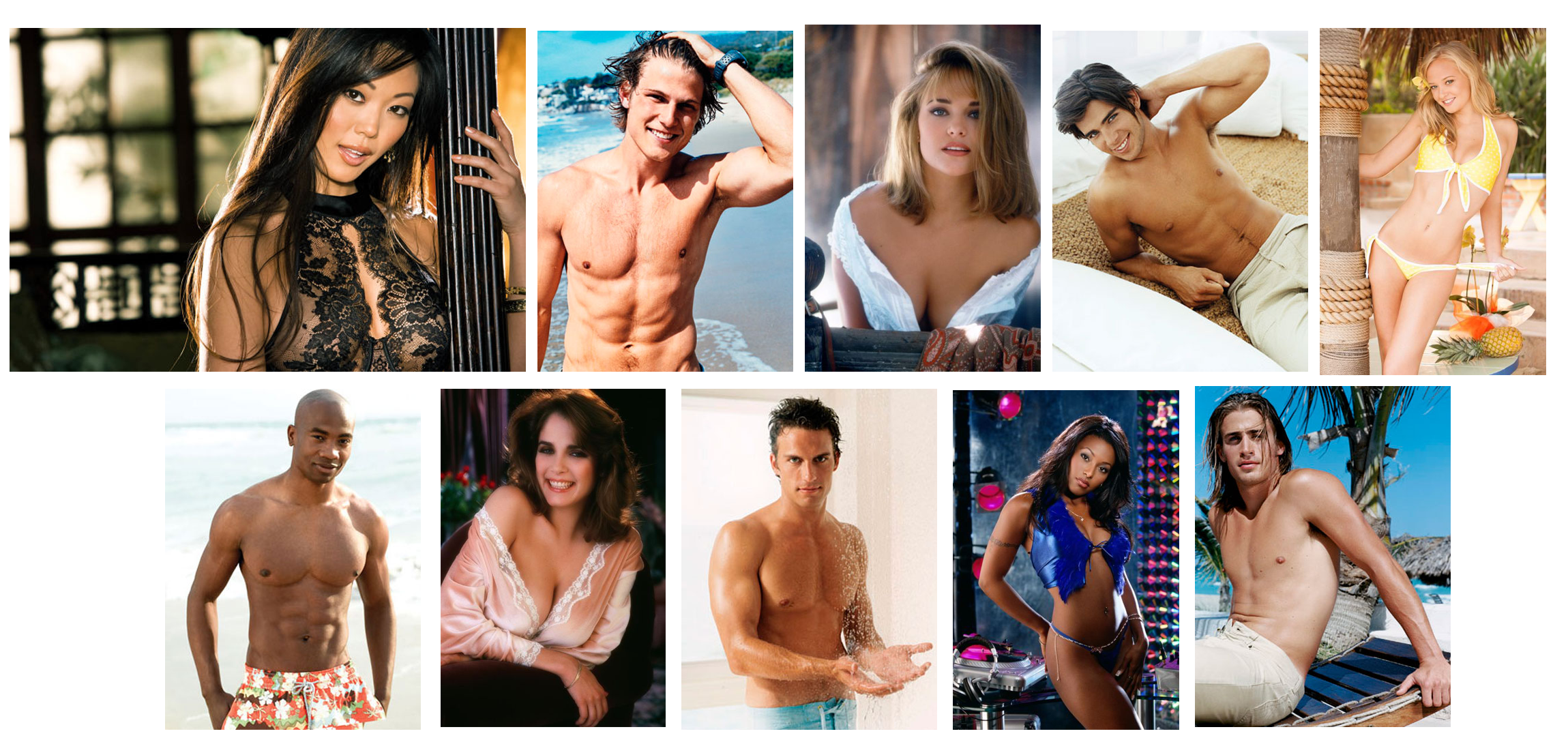
pictures
The selected pictures were aiming to elicit excitement. They were semi-nude, across different skin colors and ethnic groups. The female pictures were taken from the website playmates which is part of Playboy magazine. The male pictures were from cosmopolitan which shows a list of pictures of hot shirtless guys.

videos
The selected videos contain a neutral video and an exciting video. The exciting video was the scene Stabbed in the Back from the movie Scream 2 (2:12 minutes). This movie clip was chosen because it was not overly upsetting for participants, did not require any knowledge of the prior storyline (i.e. a stand-alone movie clip), and it was immediately suspenseful. The neutral movie was a movie clip of marine life (2:14 minutes).
Measures
- Heartbeat rate: measured by Mobi interface
- Picture attractiveness rating: on a 5-point Likert scale
- Video evaluation: on a 5-point Likert scale
- Did you experience the movie as [scary/funny/fearful/boring/exciting]?
- Emotion measure: measured with PANAS
Procedure
At the beginning, participants were instructed to place Mobi electrodes and the elastic strap (with the Tactilizer) on the left upper part of the chest.
- Task1: pictures
- For each picture, participants viewed it for 15 seconds and rated its attractiveness. Repeat ten times for ten pictures.
- After rating ten pictures, participants filled in the PANAS questionnaire.
- Task2: videos
- For each video, participants watched the whole clip, rated the evaluation questions, and filled in the PANAS questionnaire. Repeat the same procedure for both videos.
Data analysis
Analysis methods
- Heartbeat rate:
- For each picture and video, a comparison (t-test) of the average heartbeat rate between groups
- For each picture, a comparison (t-test) of the average heartbeat rate between genders
- A comparison (t-test) of the average heartbeat rate between the two videos
- Subjective measures (picture attractiveness rating, video evaluation, PANAS): one-way ANOVA or one-way ANOVA on ranks (Kruskal-Wallis H test)
Analysis tool
- Heartbeat rate
- Subjective measures
- Statistical analysis was conducted in SPSS
Results & insight
Heartbeat rate
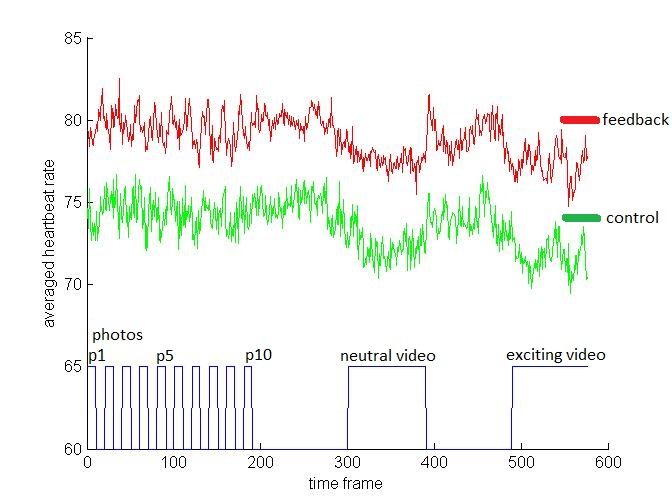
- Similar trend of average heartbeat rate between two conditions.
- The feedback group has higher heartbeat during the whole experiment.
- When watching videos -
- Exciting video: feedback group (M = 76.83, SD = 1.71) has significantly higher heartbeat than control group (M = 71.14, SD = 1.67): t(70) = −2.37, p = .02
- Neutral video: the difference is not significant between feedback and control groups.
- The difference is not significant between the two types video
- When watching pictures -
- The difference is not significant between feedback and control groups.
- The difference is not significant between female and male participants.
- Male participants had higher heartbeat when viewing male pictures (M = 77.19, SD = 2.81) than female pictures (M = 75.91, SD = 2.71): t(26) = −3.69, p < .001
(...what does this mean??)
In summary, our hypothesis is conditionally confirmed physiologically:
- Haptic feedback indeed had a higher heartbeat rate throughout the whole experiment.
- Haptic feedback significantly influenced the heartbeat when participants watched the exciting video, but not the neutral one.
Subjective measures
- When watching videos -
- Exciting video: participants feels less boring in the feedback condition (M = 1.41, SD = 0.821) compared to the control condition (M = 1.71, SD = 0.802): χ2(1) = 4.085, p = .043. No significant difference in other types feeling (i.e., scary, funny, fearful, exciting)
- Neutral video: The difference is not significant between feedback and control groups for all types feeling.
- Emotion measure: The difference is not significant between feedback and control on all PANAS scales (all p > .527).
- When watching pictures -
- The difference is not significant between feedback and control groups.
- Males rate female pictures higher than male pictures: t(26) = -4.396, p ≤ .000; whereas females rate the opposite sex higher: t(44) = 2.976, p = .005.
(...so called "Like charges repel, unlike charges attract")
In summary, our hypothesis is not supported psychologically.
Conclusion
The study did not support the original idea that synchronised cardiac feedback changes emotion, but it might still be the case that the haptic feedback influences heartbeat rates. One application of this finding I can think of is to regulate the heartbeat rate of the thrill-seeker with heart conditions (e.g., cannot afford too high heartbeat rate), without compromising on the enjoyment of the movie.
Team
Hearts and Minds is a research project by Chia-Kai Yang, Dana Rouschop, Kirsten van der Meulen, and Stephanie Dávalos Segura .